Bucks vs Suns Game 5 $500 riskfree bet, Preview, Odds, How to watch After getting off to a sweeping start in the 21 NBA Finals, the Suns let the Bucks crawl back to even the series in front of the Deer District in Milwaukee Cash in on a riskfree $500 bet for the NBA Finals Game 5 from FOX Bet!Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probabilityOdds of dying estimates assume that mortality trends change slowly over time with changes of only a few percentage points from year to year Currently, COVID19 trends are changing too rapidly to confidently anticipate future risk levels Visit the Injury Facts COVID19 page to track realtime data in the United States COVID19

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
Odds ratio vs relative risk ppt
Odds ratio vs relative risk ppt- Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeIn the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measures




Risk Differences And Rate Differences
Odds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability / (1 probability) and conversely probability = odds / (1 odds) Odds Ratio Odds ratio is the ratio of odds for the exposed group vs the unexposed groupA rate ratio, ;In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two
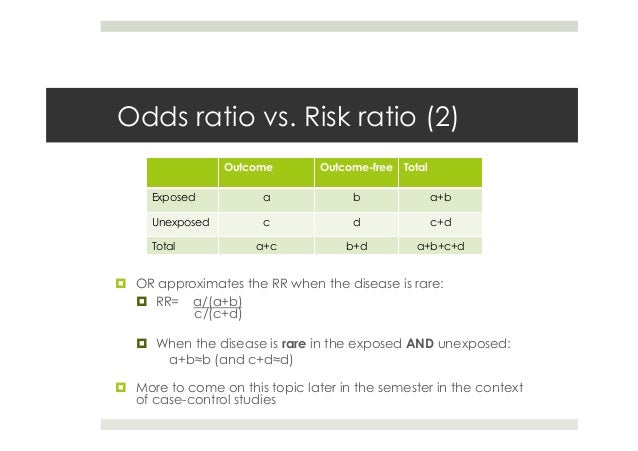
Risks and Odds When talking about the chance of something happening, eg death, hip fracture, we can talk about • risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (Denominator Numerator) 2 Two by two table Relative risks versus odds ratios Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus for the prevention of any diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use in hospital A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial study design was usedThe odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases
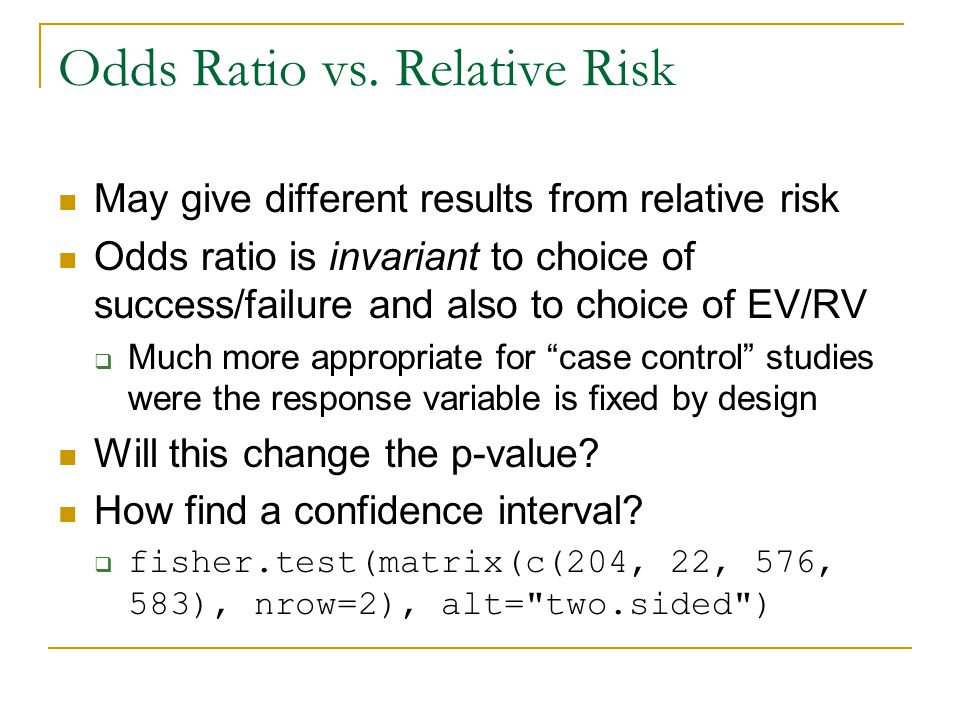
If Risk = 1, OR = Infinity Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold; The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimal




Measures Of Effect Risk Ratio Vs Rate Ratio Risk Factors Disease Risk




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Youtube
For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzedThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ; The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring




Literature Search




Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Chegg Com
Remember that in a true casecontrol study one can calculate an odds ratio, but not a risk ratio However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trialsOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 4125The odds for favorites are accompanied by a minus () sign, indicating the amount you need to stake to win $100 Meanwhile, the odds for underdogs are accompanied by a positive () sign




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event willSee all my videos at https//wwwzstatisticscom/videos/Health Stats IQ playlisthttps//youtubecom/playlist?list=PLTNMv857s9WUI5YsQMW14trmbopjZMWPa000 IntOdds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable riskor risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospective studies, attributable risk can not be calculated directly but population attributable risk can be estimated




Odds Ratios Of Risk Factors For The Severity Of Cad By Ethnicity Odds Download Scientific Diagram



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo
How to claim 1The ratio change in average risk (or odds) is not the same as the average ratio change in risk (or odds) (Table 1) An estimate of the change in average risk is useful, though it may not estimate the change expected for every individual or even for any particular individualIn the "risk" of response and a 60% increase in the "risk" of remission Risk, therefore, is used to reflect probability, regardless of the desirability or undesirability of an event 2 Relative risk is an important and commonly used Odds Ratio




Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Abbreviations Ci Confidence Interval Or Odds Ratio Low Risk Vs Download Scientific Diagram
As you can see, the interpretation of odds ratio is not as intuitive as that of the relative risk This is because most people tend to think in terms of risk (probability) and not odds So if the odds ratio is at best a mediocre version of the relative risk, then why use it at all?Even an odds ratio;The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions




Evidencebased Journal Club Intentiontotreat Odds And Risk Paul




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe odds differ from the risk, and while the odds may appear to be high, the absolute risk may be low Handling continuous input variables For continuous data (eg, age, height, or weight), it is tempting to divide the subjects into categories (eg, age >50 years vs age ≤50 years) The cutoff for "rare" differs by the specialist Here's why this works, roughly one out of 11 million people will die by a plane crash The odds of that occurring is 1 divided by 11 million minus the one unfortunate soul The risk is 1 divided by the full 11 million Either provide you a similar number with which you can formulate risk




Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
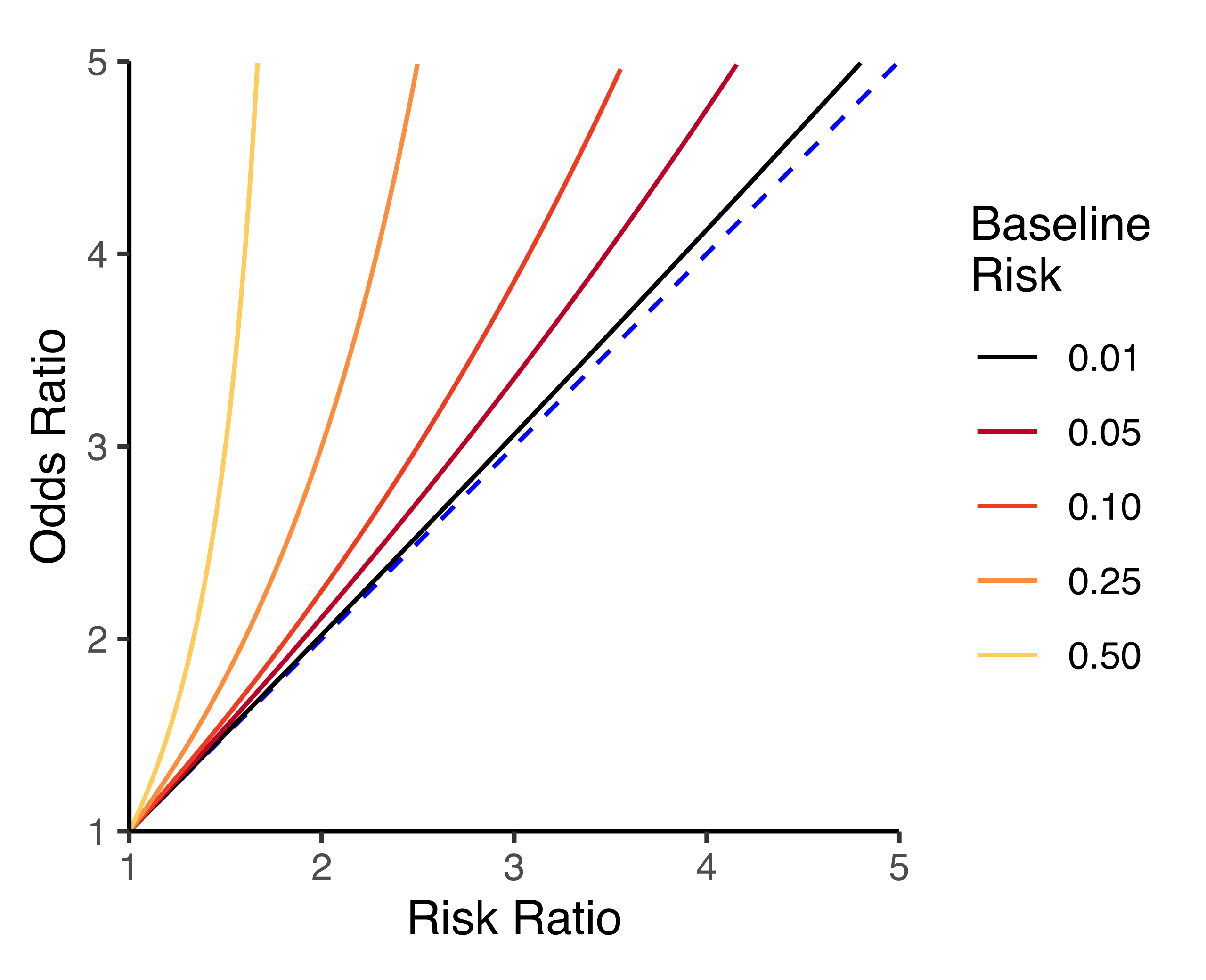
Odds, Probability, Chance Example Odds are derived from a probability as follows (Boston University) If the probability of an event is 08 (ie an 80% chance ), then the odds are 08 / (1 08) = 08 / 02 = 4, or 4 to 1 The following picture clarifies the difference between probability and odds, using an American roulette wheel with 18 The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Risk Differences And Rate Differences
The difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are largeThe odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event or disease occurring in one group to the odds occurring in another group The standard formula is X / ( 1 − X) / Y / ( 1 − Y), where X and Y are the probability of that event in the two groups, respectively In contrast, the relative risk is the risk of an event or diseaseThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers)A prevalence ratio, or ; The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download
Probability notes The game of RISK is played such that two players are allowed to "attack" and "defend" in the following ways a) the "attacker" may roll 1, 2, or 3 dice b) the "defender" may roll 1 or 2 dice c) the highest rolled attack dice is compared to the highest rolled defense dice, and 1 the attacker loses if the attack diceThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Odds are another way of expressing the likelihood of




Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk
That is defined as p/(1p) That is if p is the probability of the event of interest and (1p) is the probability that it doesn't happen So even from this simple case we see that the risk varies from 0 to 1 and the odds vary from 0 to infinity In fact, if Risk (or p) < 05, OR < 1;A terminology problem odds ratio versus odds Author William Gould, StataCorp James Hardin, StataCorp Unfortunately, the language used to describe statistical terms is not used uniformly across fields One example of this is odds and odds ratio Economists especially refer to what others call the odds as the odds ratioWhen does odds ratio approximate relative risk?




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each other Relative risk (RR) is simply the probability or relationship of two events Let's say A is event 1 and B is event 2 Risk Odds When Rolling 3 Dice against 2 When rolling 3 attacking dice against 2 defending dice attacker wins 2 3717% attacker wins 1, The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club
INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedIf Risk = 05, OR = 1;A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrence



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



54 55 Review 1 This Slide Illustrates That Even If The Disease Or Health Outcome Is Not Rare The Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio Estimate May Be Identical Or Similar Depending On The Effect Size




Measuring Of Risk




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney On Prezi Next




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare



Q Tbn And9gcq5tpzikqe8jiy9iqzxyqcbaqndofe8d2iabvvrkarpadvgvm8o Usqp Cau




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library




Odds Ratios From Univariate Regression Model Of Oasis Vs Risk Factors Download Table
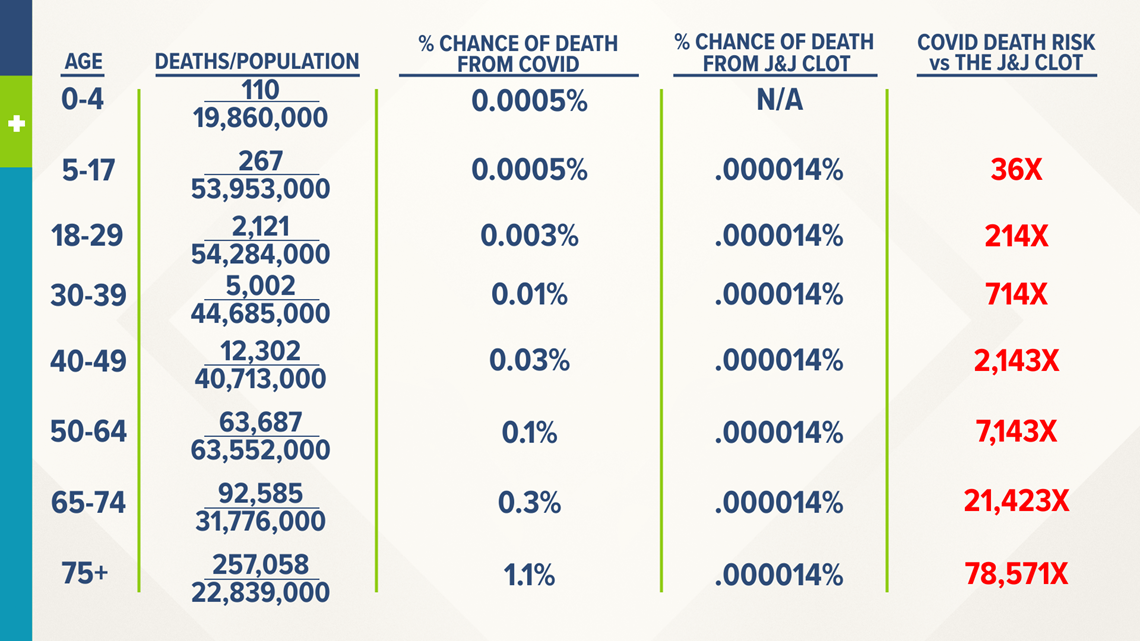



The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau




Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
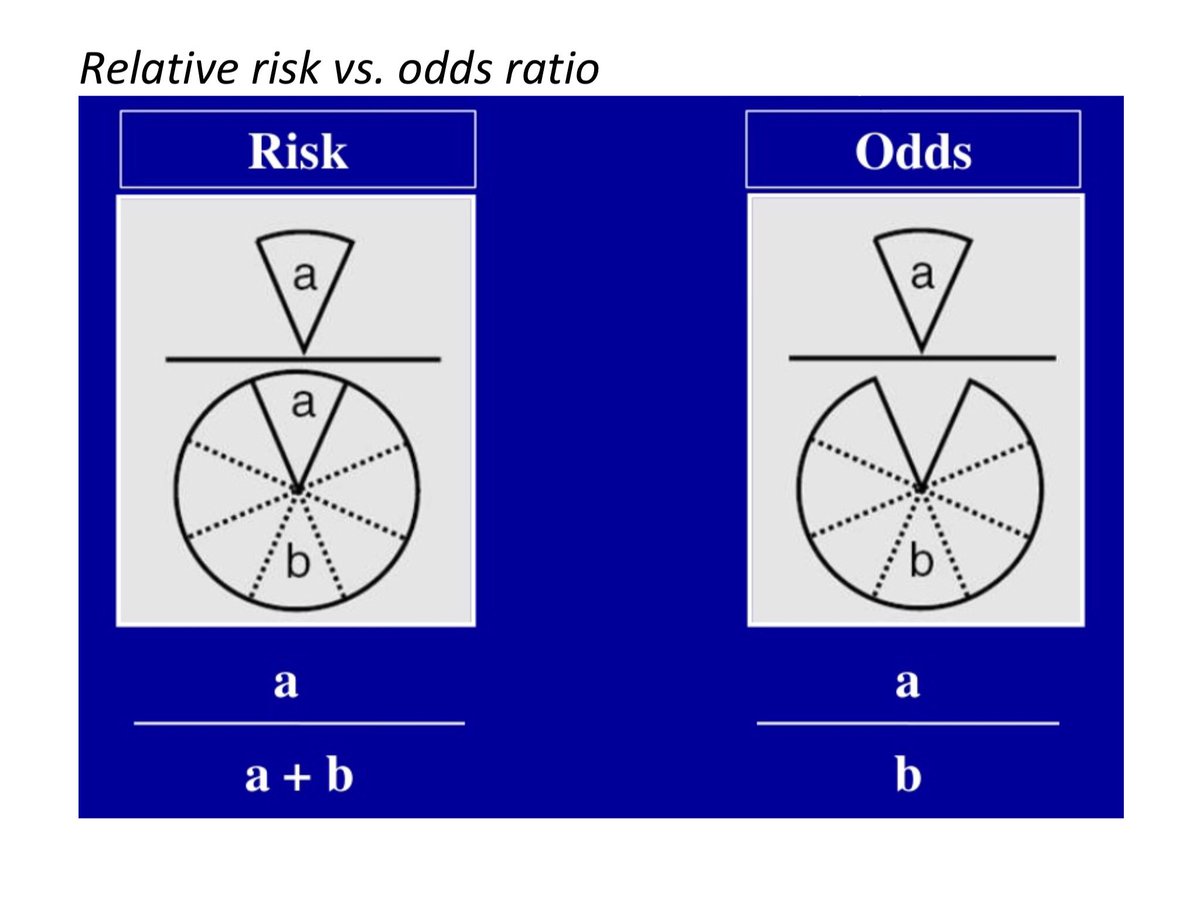



Bryan Carmody For M2s Preparing For Usmle Step 1 Epidemiology Questions Are Free Points You Don T Have To Make 2x2 Tables Or Memorize Formulae From First Aid To Calculate Or




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



1




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
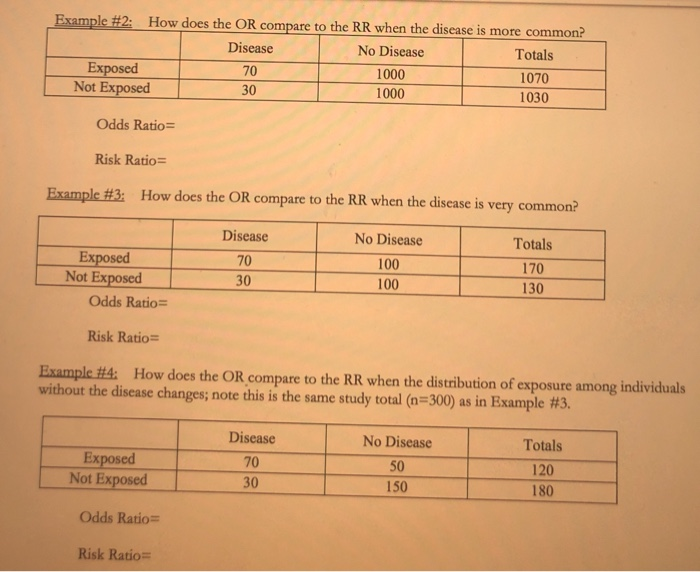



Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Casecontrol Studies For Outbreak Investigations Goals N N




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper
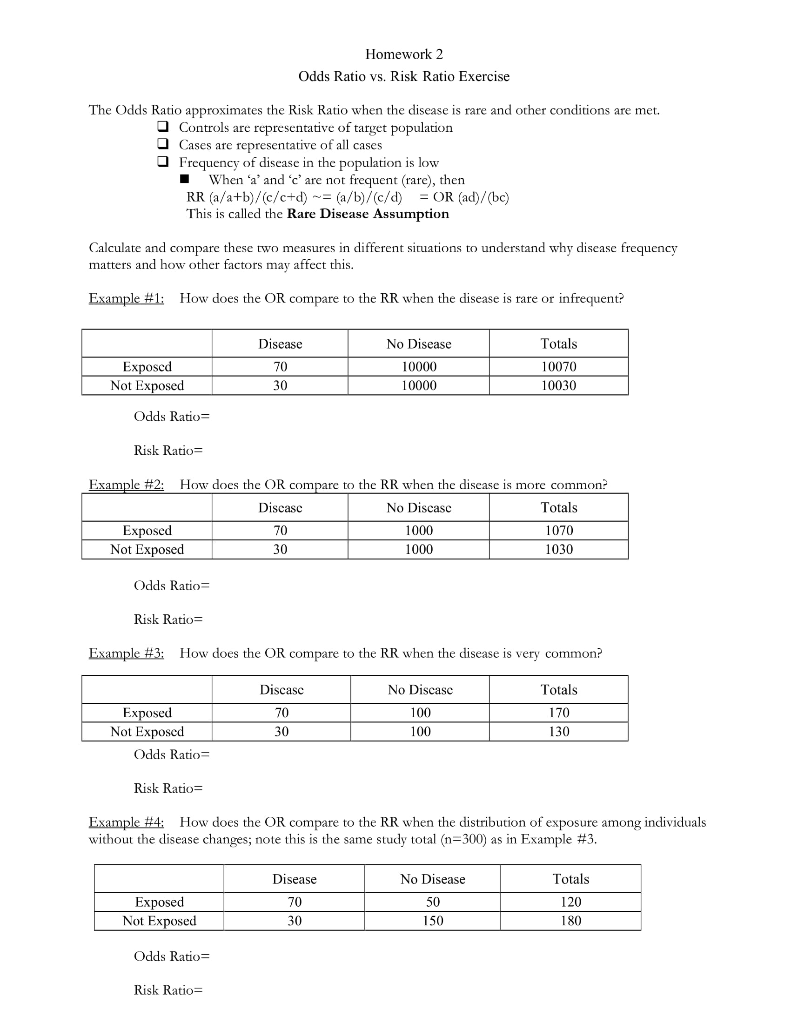



Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com



2




Comparison Of Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Based On Download Table




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



1




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




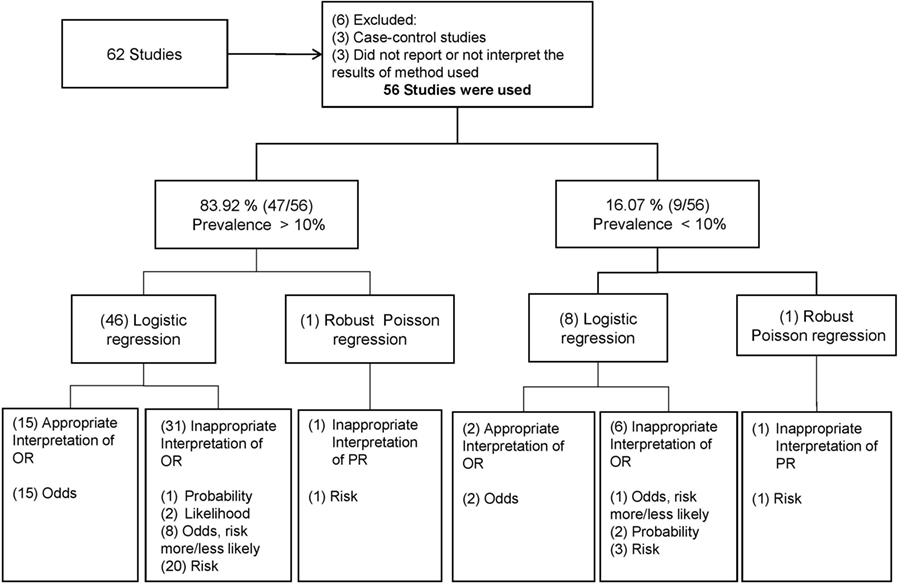
Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download



Github Flor3652 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Shiny App




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



14 Lab Slides Mo A




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
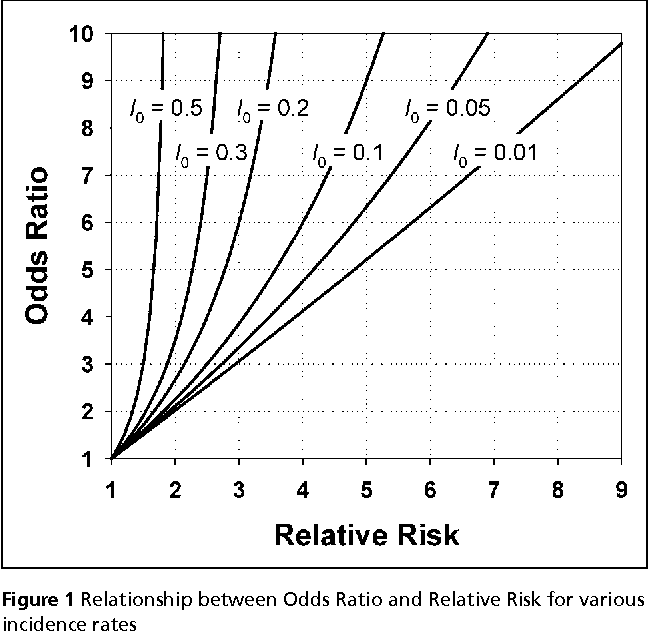



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications
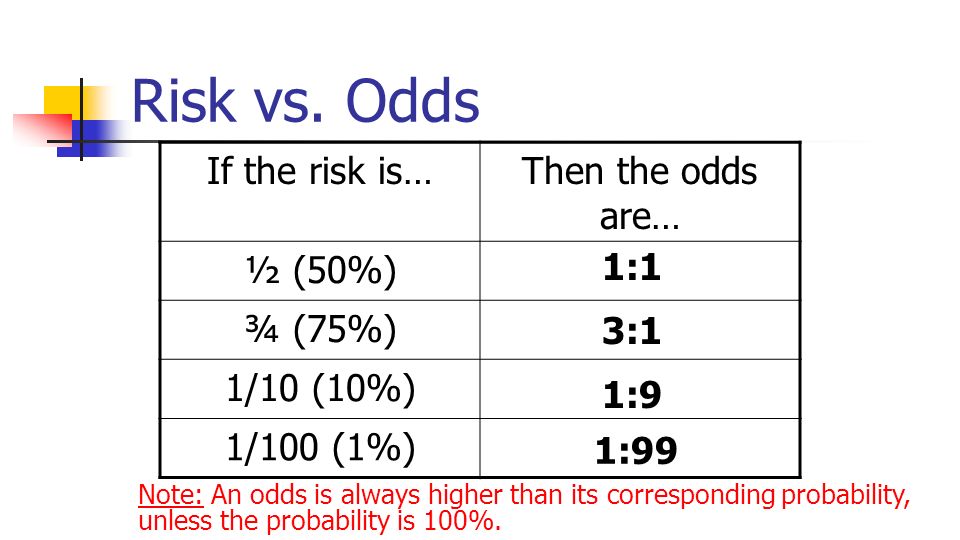



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




Observational Studies The Ebm Project




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿